POTS
What is POTS? What are POTS causes and diagnosis? What is POTS treatment and the quality of life of patients with POTS? Read all about it in this blog post.
Postural Orthostatic Tachycardia Syndrome: a Cardiovascular Autonomic Disorder
Date: 12th October 2021 Reading time: 2 mins

What is Postural Orthostatic Tachycardia Syndrome (POTS)?
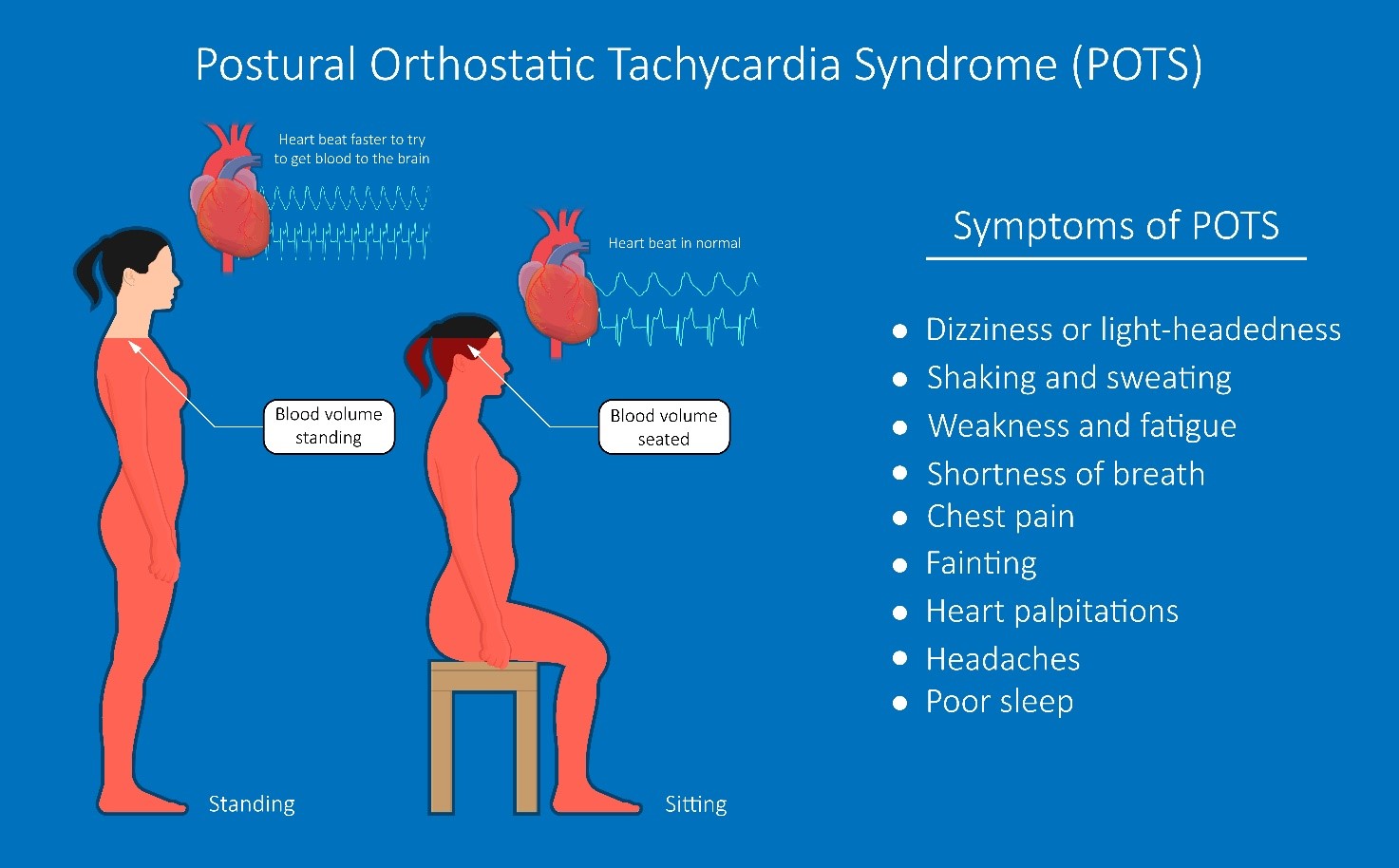
POTS is a cardiovascular autonomic disorder characterized by an excessive heart rate increase on standing and orthostatic intolerance, without orthostatic hypotension [1]. About 80% of the POTS patients are female and POTS mainly affects younger individuals (15 to 45 years old). The prevalence of POTS ranges between 0.2% and 1.0% in developed countries. The most common complaints of patients with POTS are dizziness, weakness, rapid heartbeat, and palpitation on standing. [2]
What are POTS causes?
The aetiology of POTS is largely unknown. The three main hypotheses include:
1: an autoimmune disorder,
2: abnormally increased sympathetic activity and catecholamine excess, and
3: sympathetic denervation leading to central hypovolaemia and reflex tachycardia [2].
Despite its relatively common presentation in the population, POTS is a relatively misunderstood autonomic disease. Researchers and clinicians struggle to distinguish, diagnose and treat those affected by the condition. A complicating factor is heterogeneity of symptoms that may mask the underlying POTS and divert the clinician’s attention towards other conditions with a similar presentation [1, 2].
POTS diagnosis
The head-up tilt test and the active stand test are commonly used to diagnose POTS. Both of these autonomic function tests should be performed with non-invasive beat-to-beat hemodynamic monitoring!
POTS treatment and quality of life
The most common treatments for POTS include increasing fluid intake, increasing salt, wearing compression stockings, raising the head of the bed (to conserve blood volume), reclined exercises such as rowing, recumbent bicycling and swimming, a healthy diet; avoiding substances and situations that worsen orthostatic symptoms; and finally, the addition of medications meant to improve symptoms [3]. Some patients have mild symptoms and can continue with normal work, school, social and recreational activities. But for others, symptoms may be so severe that normal life activities, such as eating, sitting upright, walking or standing can be significantly limited! Approximately 25% of POTS patients are disabled and unable to work. Researchers found that quality-of-life in POTS patients is comparable to patients on dialysis for kidney failure [3].

Want to learn more about POTS?
Watch the open-access educational webinar POTS syndrome: overview and focus on non-pharmacological approaches! Satish Raj, PhD and Kate Bourne, BSc from the University of Calgary briefly overviewed POTS, including diagnostic criteria, common symptoms and highlights from a large patient community survey. They also outlined some of the non-pharmacological approaches to the management of the patient with POTS. This webinar was hosted by InsideScientific and sponsored by Finapres Medical Systems!
More questions? Do not hesitate to contact us!
References
- Raj, S.R. “The postural tachycardia syndrome (POTS): pathophysiology, diagnosis & management” Indian pacing and electrophysiology journal (2006)
- Fedorowski, A. “Postural orthostatic tachycardia syndrome: clinical presentation, aetiology and management” Journal of internal medicine (2019)
- Dysautonomia international, POTS (2020), http://www.dysautonomiainternational.org/page.php?ID=30