What is Dysautonomia?
Date: 14th February 2022 Reading time: 3-4 mins
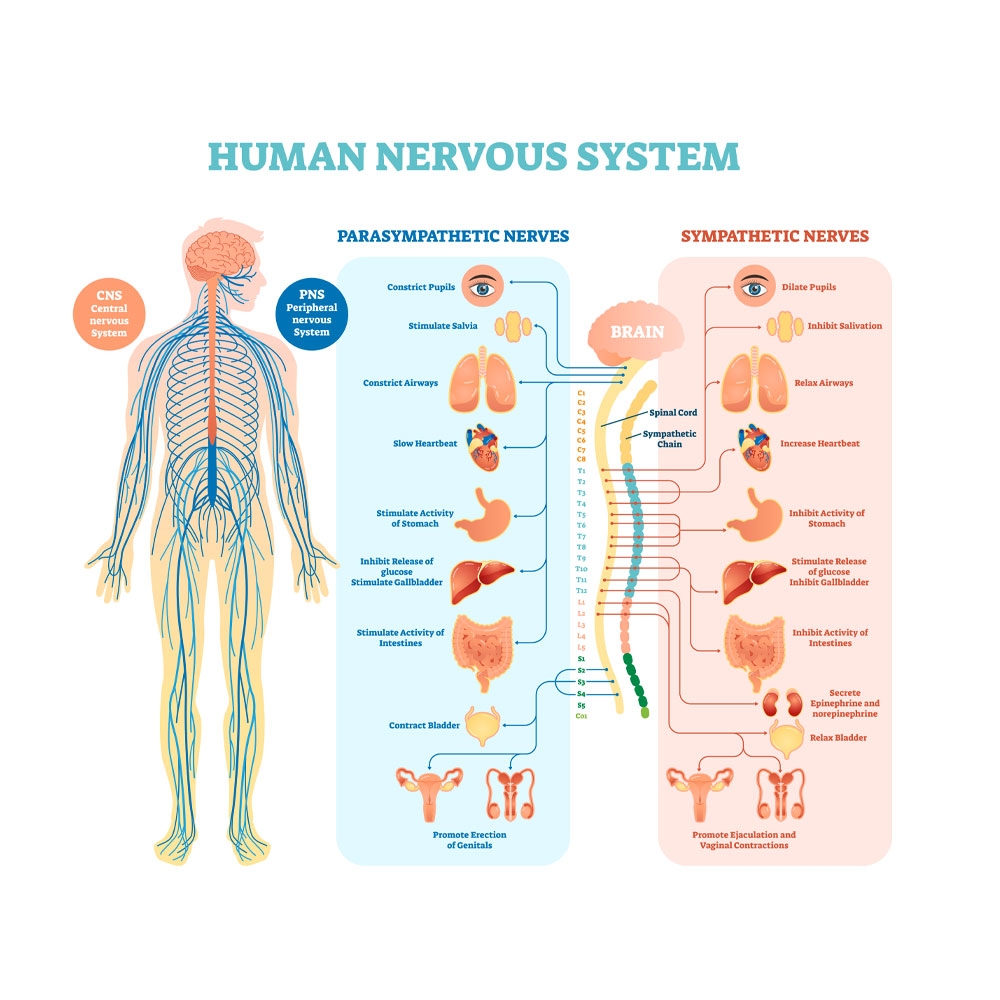
Dysautonomia: Dysfunction of the Autonomic Nervous System (ANS)
The Autonomic Nervous System (ANS) is the part of your body that controls many functions like heart rate, blood pressure, breathing, digestion etcetera. These functions are controlled involuntary via the so-called sympathetic and parasympathetic pathways. Involuntary means that these body functions are not controlled consciously.
When the ANS doesn’t function as it should, this is called Dysautonomia, Autonomic Dysfunction or Autonomic Neuropathy. Dysautonomia is a general term for the group of autonomic disorders. Worldwide, it affects more than 70 million people and it can be present at birth, appear gradually or suddenly appear at any age.
Primary Dysautonomia and Secondary Dysautonomia
Dysautonomia can occur as its own disease: Primary Dysautonomia. This is the case in Vasovagal Syncope, Postural Orthostatic Tachycardia Syndrome (POTS), Familial dysautonomia (FD), Multiple system atrophy (MSA) and pure autonomic failure.
Dysautonomia can also occur as a condition of another disease: Secondary Dysautonomia. There are many diseases in which (some) patients suffer from Secondary Dysautonomia, including:
- Parkinson’s disease [1]
- Long COVID [2]
- Diabetes [3]
- Muscular Sclerosis (MS)
- Dementia [4]
- Ehlers-Danlos syndrome [5]
- Guillain-Barré syndrome [6]
- etc.
Causes and Symptoms of Dysautonomia
Dysautonomia occurs when the nerves in the ANS are not able to communicate as they should. This implicates that messages through the ANS are not send or received properly and this can cause a variety of symptoms. A common symptom of dysautonomia is Orthostatic Intolerance. This means that a subject develops symptoms like dizziness or fainting when standing upright, which are relieved when reclining.

Other symptoms of dysautonomia include:
- Large swings in heart rate and blood pressure
- Syncope, loss of consciousness
- Balance problems
- Dizziness, lightheadedness, vertigo
- Visual disturbances
- Swings in body and skin temperature
- Migraines or frequent headaches
Diagnosis of Dysautonomia
There are many different tests that can be performed to diagnose dysautonomia, depending on the patients’ complaints and differential diagnosis after collecting anamneses, patient history and physical examination. The diagnostic workup could consist of blood tests, sweating tests, ECG monitoring, and cardiovascular autonomic function tests with beat-to-beat blood pressure monitoring.

Examples of cardiovascular autonomic functions tests are the:
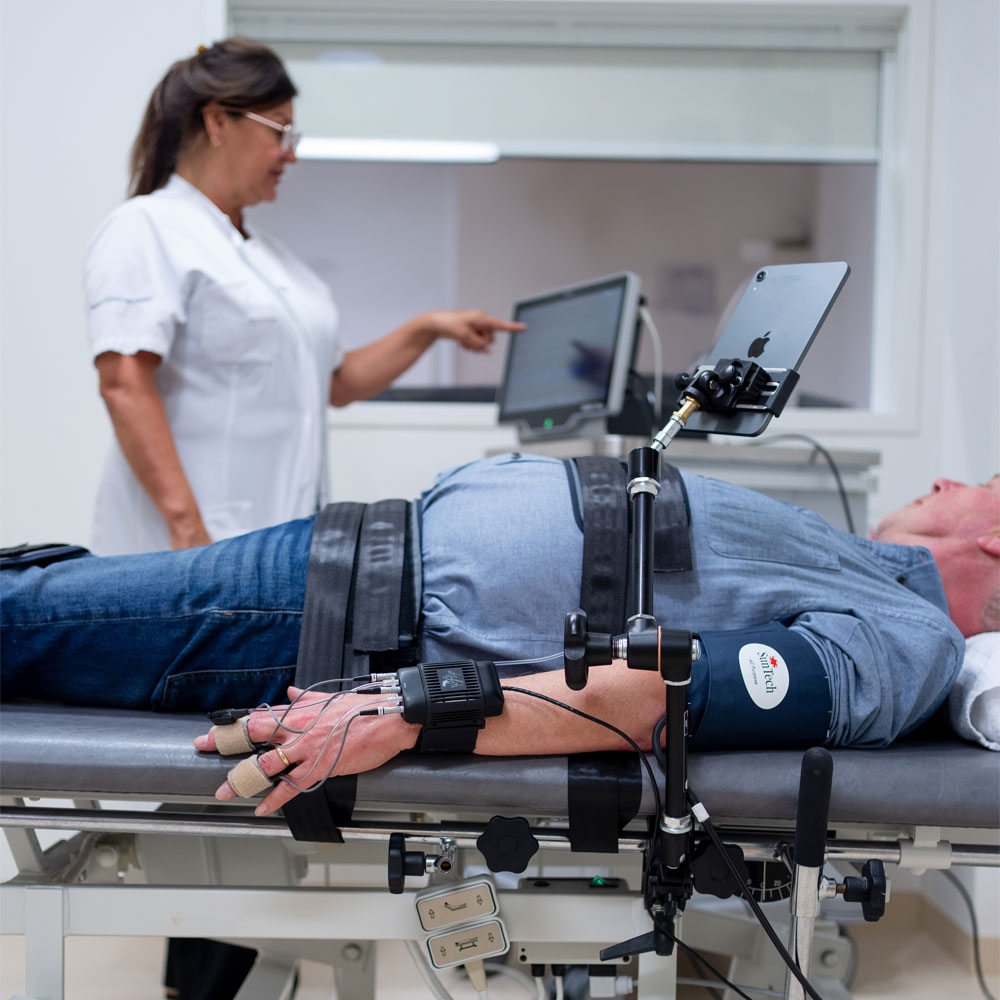
Tilt testing with the Finapres® NOVA with Guided Autonomic Testing (GAT) application
References
- Jain, Samay, and David S. Goldstein. “Cardiovascular dysautonomia in Parkinson disease: from pathophysiology to pathogenesis.” Neurobiology of disease (2012)
- Dani, Melanie, et al. “Autonomic dysfunction in ‘long COVID’: rationale, physiology and management strategies.” Clinical Medicine (2021)
- Bernardi, Luciano, et al. “Methods of investigation for cardiac autonomic dysfunction in human research studies.” Diabetes/metabolism research and reviews (2011)
- Femminella, Grazia Daniela, et al. “Autonomic dysfunction in Alzheimer’s disease: tools for assessment and review of the literature.” Journal of Alzheimer’s Disease (2014)
- De Wandele, Inge, et al. “Dysautonomia and its underlying mechanisms in the hypermobility type of Ehlers–Danlos syndrome.” Seminars in arthritis and rheumatism (2014)
- Chakraborty, Tia, et al. “Dysautonomia in Guillain–Barré syndrome: prevalence, clinical spectrum, and outcomes.” Neurocritical care (2020)
